Superquadric Representation
Superquadrics (SQs) are a compact family of parametric primitives that can model cylinders, spheres, ellipsoids, rounded boxes, and more, by varying a small set of shape exponents and scales. An SQ can be defined by the following implicit function; the surface is where the function equals zero, points with negative value are inside, and positive value are outside:
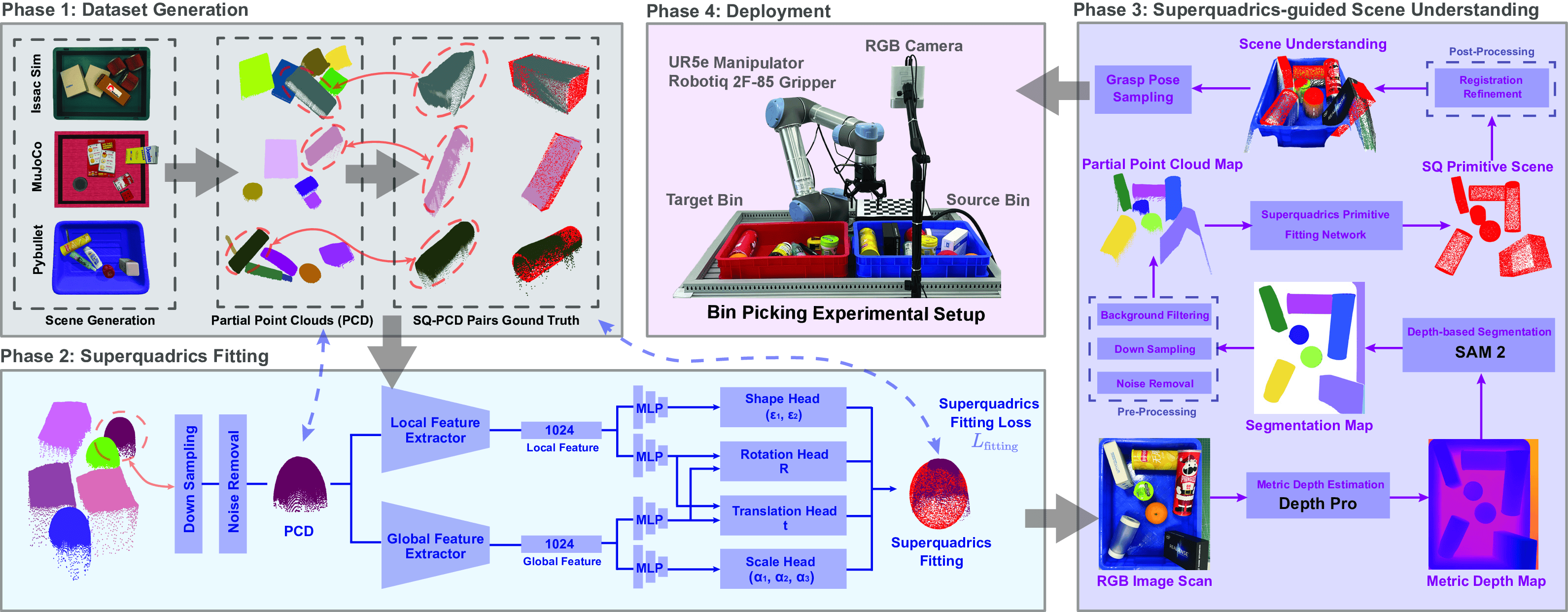
\begin{equation} F(\mathbf{x}) \;=\; \left( \left|\frac{x}{a_x}\right|^{\frac{2}{\epsilon_2}} +\left|\frac{y}{a_y}\right|^{\frac{2}{\epsilon_2}} \right)^{\frac{\epsilon_2}{\epsilon_1}} \;+\; \left|\frac{z}{a_z}\right|^{\frac{2}{\epsilon_1}} \;-\;1. \label{eq:sq-implicit} \end{equation}Here $\mathbf{x}=[x,y,z]^{\top}\!\in\mathbb{R}^3$ is expressed in the SQ’s local coordinates; $a_x,a_y,a_z>0$ are axis scales; and $\epsilon_1,\epsilon_2\ge 0$ are shape exponents controlling curvature and “boxiness.” Smaller exponents yield rounder shapes; larger values sharpen faces and edges. The image below visualizes how varying $(\epsilon_1,\epsilon_2)$ changes the shape.
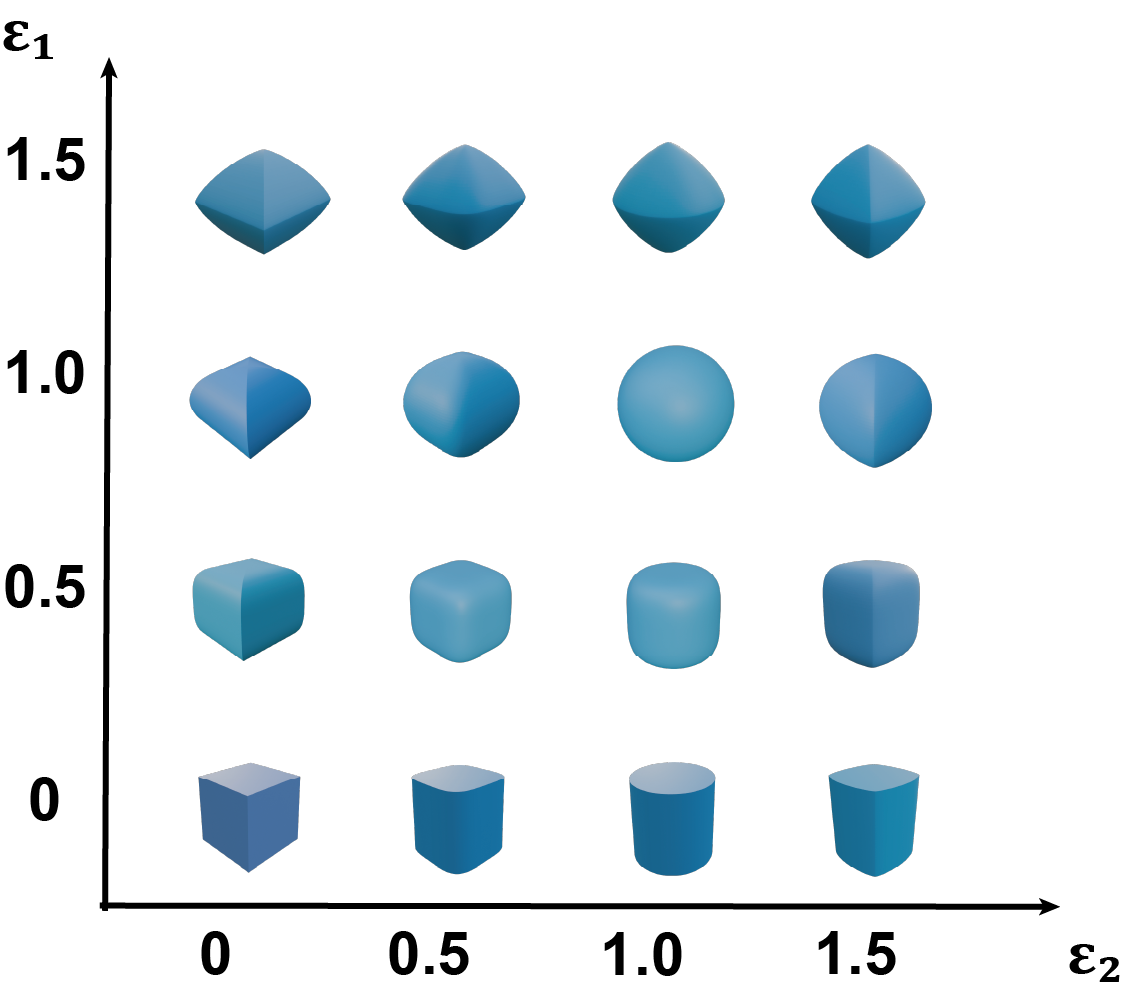
For surface sampling and rendering, it is convenient to use the following explicit (parametric) form:
\begin{equation} \mathbf{r}(\eta,\omega) \;=\; \begin{bmatrix} a_x\,\cos^{\epsilon_1}\!\eta\,\cos^{\epsilon_2}\!\omega \\ a_y\,\cos^{\epsilon_1}\!\eta\,\sin^{\epsilon_2}\!\omega \\ a_z\,\sin^{\epsilon_1}\!\eta \end{bmatrix}, \qquad \eta\in\left[-\tfrac{\pi}{2},\,\tfrac{\pi}{2}\right],\; \omega\in[-\pi,\,\pi]. \label{eq:sq-explicit} \end{equation}A full superquadric instance is determined by 11 parameters: three scales $(a_x,a_y,a_z)$, two shape exponents $(\epsilon_1,\epsilon_2)$, and a 6-DoF pose in 3D space. The pose is written as $\mathbf{g}=[\mathbf{R},\mathbf{t}] \in SE(3)$ with $\mathbf{R}\in SO(3)$ the rotation and $\mathbf{t}\in\mathbb{R}^3$ the translation. Equations \eqref{eq:sq-implicit}–\eqref{eq:sq-explicit} are the forms we use for inference, fitting, and point-cloud sampling.